In 2025, Gmail remains the world’s email gatekeeper, scanning over 300 billion messages every day. What most marketers, businesses, and even IT teams don’t realize is that Google now blocks or filters out more than 15 billion spam emails daily – a figure confirmed by Google’s own Postmaster team. That means if your email authentication isn’t airtight, there’s a good chance your carefully crafted messages never reach the inbox at all.
Here’s the truth: Gmail’s anti-spam rules have never been stricter. As of 2025, senders are required to comply with updated DMARC, SPF, and DKIM authentication standards. Ignore these rules, and your emails don’t just land in promotions – they may be quarantined, bounced, or deleted before users ever see them. This isn’t just about compliance – it’s about survival in a crowded digital inbox where trust signals are the difference between visibility and invisibility.
The problem is that most businesses set up authentication wrong. They add an SPF record but forget about alignment. They enable DKIM but never rotate keys. They publish a DMARC policy but leave it in “none” mode for years, thinking it’s good enough. These mistakes kill deliverability and silently erode your sender reputation. In fact, according to Cisco’s 2024 Email Security Report, over 91% of phishing attempts exploit poor or missing authentication setups – proof that mistakes cost more than just inbox placement; they open the door to fraud.
After more than a decade of hands-on experience helping businesses fix deliverability nightmares, I’ve seen the same frustrations play out again and again: messages blocked, client updates lost, revenue campaigns crippled. That’s why I created this guide – the definitive Gmail Rules 2025 resource.
Unlike quick-fix blog posts, this is an end-to-end playbook that covers everything:
- DMARC, SPF, DKIM basics explained in depth
- Step-by-step authentication setup for Gmail
- Best practices and mistakes to avoid in 2025
- The exact tools, strategies, and tips professionals use
- Advanced authentication techniques for experts
If you’re tired of guessing why Gmail keeps flagging your emails, this guide gives you the clarity and the roadmap you need. By the end, you’ll know exactly how to set up, optimize, and future-proof your email authentication so your messages consistently land where they belong – the inbox.
Understanding Gmail Rules 2025 & DMARC, SPF, DKIM Basics
To build long-term Gmail deliverability in 2025, you first need to understand the foundation of modern email authentication. Too many senders jump straight into tools and tactics without grasping the underlying mechanics. That’s why their deliverability tanks. This section explains exactly what Gmail looks for, how DMARC, SPF, and DKIM work together, and why skipping even one piece can cause your emails to fail.
What Gmail Really Wants in 2025
Gmail’s anti-spam rules have evolved from simple keyword filters into AI-driven authentication checks. Every email you send is scored based on three layers:
- Identity Verification – Can Gmail confirm that you are who you claim to be?
- Policy Enforcement – Do your domain’s DNS records (SPF, DKIM, DMARC) allow you to send this message?
- Reputation Signals – Do recipients engage, open, click, or report your messages as spam?
If you fail on authentication, reputation doesn’t even matter. Gmail blocks you before you reach the inbox.
According to Google’s 2025 Sender Guidelines, all bulk senders must:
- Publish valid SPF (Sender Policy Framework) records.
- Enable DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) signatures.
- Deploy DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) with at least a “p=quarantine” policy.
Miss any of these steps, and Gmail will either flag your domain as high risk or reject your messages outright.
DMARC, SPF, DKIM Basics – Explained Simply
Think of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC as the passport, signature, and border patrol of email:
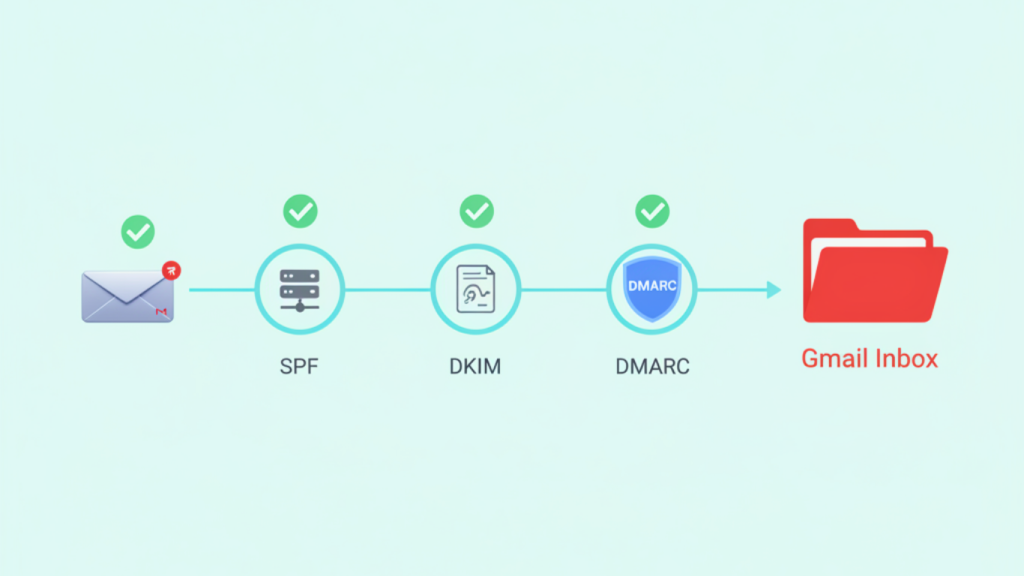
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) – Like a passport stamp, SPF verifies that the server sending your email is authorized by your domain. If your domain says only Google servers can send email on its behalf, and a spammer tries sending from Russia, Gmail rejects it.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) – This is your cryptographic signature. It ensures that the email hasn’t been altered in transit. Imagine signing every letter with a unique seal – Gmail checks if that seal matches the one registered for your domain.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) – DMARC is the border patrol. It enforces rules: if SPF or DKIM fail, Gmail asks, “What should I do with this email?” (none, quarantine, or reject). It also generates reports so you can monitor fraud attempts and misconfigurations.
When combined, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC create a chain of trust. Without this chain, Gmail assumes your messages could be spam or phishing.
Why Most People Fail at Email Authentication
Even though these systems aren’t new, businesses still fail to configure them correctly. The most common DMARC, SPF, DKIM mistakes include:
- SPF record too long (more than 10 DNS lookups). Gmail ignores it.
- DKIM key misalignment (signing with a subdomain while sending from the root domain).
- DMARC stuck at “none” forever – meaning you’re monitoring but not enforcing.
- Multiple SPF records instead of one consolidated version.
- Forgetting to rotate DKIM keys (Google recommends every 6–12 months).
These errors don’t just hurt deliverability; they open your domain to spoofing. In 2024, Proofpoint reported that 89% of Fortune 500 companies still had misconfigured or unenforced DMARC, making them prime targets for phishing. If the giants fail, small businesses are even more vulnerable.
Myths & Misconceptions to Debunk
Let’s bust a few Gmail deliverability myths that kill results:
- “SPF alone is enough.” False. Gmail requires SPF, DKIM, and DMARC together. One missing breaks the chain.
- “A DMARC policy of none is safe.” Wrong. It’s just monitoring – Gmail can still let spoofed emails through.
- “DKIM breaks email forwarding.” Not true if properly aligned.
- “Once set, never touch authentication records.” Dangerous. Records must be updated as you add tools (CRM, newsletter platforms, etc.).
Why This Foundation Matters
Here’s the bottom line: without authentication, nothing else works. You can write the most persuasive subject line, create the best offer, or even warm up your domain – but Gmail will still reject you if your DMARC, SPF, and DKIM aren’t properly set up.
This is why you must master the basics first before moving into advanced strategies. Think of this as your email authentication firewall. Get it wrong, and you’re locked out of inboxes. Get it right, and Gmail rewards you with consistent deliverability, trust, and engagement.
The 9 Essential Elements for Gmail Deliverability Success in 2025
Gmail’s updated anti-spam rules in 2025 mean that deliverability is no longer just about content quality – it’s about building trust through authentication, reputation, and consistent sender practices. Below are the nine essential elements that separate senders who land in the inbox from those stuck in spam or blocked entirely.
1. How to Set Up DMARC, SPF, and DKIM Correctly
Why it’s critical: Gmail authentication rules demand all three protocols working together. If even one is missing or misconfigured, Gmail treats your domain as suspicious.
Step-by-step implementation:
SPF – Publish one valid SPF record in your DNS. Example:
v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com include:sendgrid.net -all
- Limit to 10 lookups. Consolidate if you use multiple services.
- DKIM – Enable DKIM signing in Google Workspace or your ESP. Use 2048-bit keys (stronger than 1024). Rotate keys every 6–12 months.
DMARC – Start with monitoring mode:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com
- Move to p=quarantine → then p=reject as you gain confidence.
Common mistakes to avoid:
- Multiple SPF records.
- Forgetting to add reporting emails in DMARC.
- Using weak 1024-bit DKIM keys.
Pro tip: Use Google Postmaster Tools to check alignment and monitor spam rates.
2. Best Gmail Anti-Spam Practices
Why it matters: Authentication opens the door, but Gmail’s engagement filters decide if you stay in the inbox.
Strategies that work in 2025:
- Send only to engaged lists (Gmail tracks opens, clicks, and spam complaints).
- Avoid spam-triggering tactics (all caps, deceptive subject lines).
- Segment sending by domain (separate transactional and marketing emails).
- Limit daily sends during warm-up (start small, scale gradually).
Example: A B2B SaaS company reduced spam complaints by 62% after segmenting inactive Gmail users and sending re-engagement campaigns separately.
3. SPF & DKIM Tools for Gmail
Why it’s critical: DNS records are technical and easy to misconfigure. Tools make validation simple.
Recommended free tools:
- MXToolbox – Check SPF/DKIM/DMARC instantly.
- Google Admin Toolbox Dig – DNS record lookup for Gmail.
- DMARC Analyzer (free tier) – Visualizes reports.
Paid/pro solutions:
- GlockApps – Inbox placement testing.
- Dmarcian – Advanced DMARC analytics.
- Proofpoint Email Fraud Defense – Enterprise-grade.
Pro tip: Run a weekly automated check. Gmail updates filtering regularly, and records can break after DNS changes.
4. DMARC Strategies for Email Security
Why it matters: DMARC isn’t just about Gmail deliverability – it prevents phishing and brand impersonation.
Strategic rollout:
- Start at p=none to collect reports.
- Analyze data to find unauthorized senders.
- Shift to p=quarantine to block suspicious mail.
- End at p=reject for full enforcement.
Example: Bank of America publicly stated that DMARC enforcement reduced spoofing attempts by 97%.
Pro tip: Use BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification) with DMARC enforcement to display your logo in Gmail inboxes.
5. Email Authentication for Beginners
Why it’s critical: Many small businesses just need a simple roadmap.
Beginner tips:
- Use Google Workspace’s built-in SPF/DKIM generator.
- Monitor with Postmaster Tools – free and beginner-friendly.
- Avoid free sending domains (like Gmail.com). Always use your own domain.
Common beginner mistake: Thinking Mailchimp/HubSpot handles all authentication. You must still update your DNS records.
6. Advanced Gmail Authentication Tactics
For experts who want more than the basics:
- ARC (Authenticated Received Chain): Preserves authentication across email forwarding.
- Key Rotation Automation: Use APIs to rotate DKIM every 90 days.
- Custom DMARC Reporting Dashboards: Visualize threats and delivery performance.
Pro tip: Pair DMARC enforcement with third-party monitoring for phishing detection.
7. How to Monitor Gmail Deliverability Metrics
Why it matters: You can’t fix what you don’t track.
Tools to monitor:
- Google Postmaster Tools – Spam complaint rates, domain reputation, IP reputation.
- Postmark DMARC digests – Simplified daily insights.
- Mailgun Deliverability Dashboard – For high-volume senders.
Metrics to watch:
- Spam complaint rate: Keep below 0.1%.
- Domain reputation: Aim for “High.”
- Authentication alignment: 100% DKIM/SPF pass rates.
8. Troubleshooting Common SPF/DKIM Mistakes
Frequent errors:
- SPF records with more than 10 lookups.
- Missing “-all” at the end of SPF (use -all not ~all).
- DKIM not enabled for all sending platforms.
- Old marketing platforms still listed in DNS.
Quick fix checklist:
- Validate records weekly.
- Audit all services sending mail (CRM, marketing, invoicing).
- Remove unused ESPs from SPF.
9. Real-World Gmail Deliverability Examples
Case Study 1: A retail brand saw a 41% increase in Gmail inbox placement after moving DMARC from “none” to “quarantine.”
Case Study 2: A SaaS startup reduced bounce rates by 28% after consolidating multiple SPF records into one.
Case Study 3: A university protected its .edu domain from thousands of phishing attempts by deploying DMARC + BIMI, restoring trust in its communications.
Your Complete Gmail Authentication Toolkit
Configuring DMARC, SPF, and DKIM is one thing – keeping them optimized and monitored is another. Gmail’s rules in 2025 demand continuous compliance, not just a one-time setup. The right toolkit saves time, prevents mistakes, and ensures you stay ahead of Gmail’s evolving filters.
Below is the definitive toolkit – divided into Free Tools, Paid Solutions, and Enterprise Platforms – with details on what they do, who should use them, and why they matter.
Free Tools (Beginner-Friendly Essentials)
1. Google Postmaster Tools
- What it does: Provides direct insights into Gmail deliverability – spam rates, domain reputation, and IP reputation.
- Best for: All senders (beginners to advanced).
- Pros: Free, official Google data.
- Cons: Data can lag by 24 hours.
2. MXToolbox
- What it does: Quick SPF, DKIM, and DMARC lookup. Detects configuration errors.
- Best for: Beginners needing validation.
- Pros: Simple and accurate.
- Cons: Limited reporting depth.
3. DMARC Analyzer (Free Tier)
- What it does: Parses DMARC XML reports into human-readable dashboards.
- Best for: Beginners monitoring new DMARC policies.
- Pros: Clear visualization.
- Cons: Limited features unless upgraded.
4. Google Admin Toolbox DIG
- What it does: DNS record lookups. Essential for Gmail admins.
- Best for: Workspace users.
- Pros: Official Google support tool.
- Cons: Technical interface.
Paid Tools (Advanced Monitoring & Testing)
1. GlockApps
- What it does: Inbox placement testing across Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo.
- Best for: Marketers sending campaigns.
- Pricing: From $59/month.
- Pros: Tests across ISPs.
- Cons: Limited free usage.
2. Dmarcian
- What it does: Comprehensive DMARC analytics and compliance reporting.
- Best for: SMEs and security teams.
- Pricing: From $19/month.
- Pros: Visualizes threats clearly.
- Cons: Overwhelming for beginners.
3. MailTester
- What it does: Rates deliverability score, checks SPF/DKIM/DMARC.
- Best for: Small businesses.
- Pricing: From $30/month.
- Pros: Easy to use.
- Cons: Less granular analytics.
4. SendForensics
- What it does: Real-time deliverability testing, spam filter simulation.
- Best for: Growing brands.
- Pricing: From $49/month.
- Pros: Strong predictive analysis.
- Cons: Slight learning curve.
Premium & Enterprise Solutions (Full Security Suites)
1. Proofpoint Email Fraud Defense
- What it does: Enterprise-grade DMARC enforcement with phishing defense.
- Best for: Enterprises and financial institutions.
- Pricing: Custom enterprise pricing.
- Pros: Industry-leading fraud prevention.
- Cons: Expensive.
2. Mimecast Email Security
- What it does: End-to-end email protection, including DMARC management.
- Best for: Large corporations.
- Pros: Strong anti-phishing and compliance features.
- Cons: Heavy setup requirements.
3. Barracuda Email Protection
- What it does: Combines SPF/DKIM/DMARC management with spam filtering.
- Best for: Enterprises seeking all-in-one security.
- Pros: Great reporting + monitoring.
- Cons: Requires IT expertise.
4. Valimail Authenticate
- What it does: Automates DMARC setup and enforcement.
- Best for: Organizations with multiple sending services.
- Pros: Automation saves hours.
- Cons: Costly for small senders.
Choosing the Right Tool for You
- Beginners / Small Businesses: Google Postmaster Tools + MXToolbox + DMARC Analyzer.
- Growing Brands: GlockApps + Dmarcian for ongoing deliverability testing.
- Enterprises: Proofpoint or Mimecast for enterprise-grade fraud protection.
Pro Tip: No single tool covers everything. Use a combination: one for DNS checks (MXToolbox), one for deliverability analytics (GlockApps), and one for compliance (Dmarcian/Proofpoint).
Your 30-Day Gmail Deliverability Action Plan
Getting Gmail authentication right is not a “set it and forget it” task. Gmail’s 2025 rules require a structured rollout: first building a foundation, then implementing authentication, followed by optimization and advanced scaling. Below is your 30-day blueprint – divided into four weekly phases – that takes you from zero to fully compliant, optimized, and future-proof.

Week 1: Foundation Setup
Goals: Establish authentication records and lay the groundwork.
Action Items:
- Audit your DNS records.
- Check for existing SPF/DKIM/DMARC entries with MXToolbox.
- Remove duplicate SPF records.
- Set up SPF correctly.
- Add one record with all sending services (ESP, CRM, etc.).
- Add one record with all sending services (ESP, CRM, etc.).
Example:
v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com include:sendgrid.net -all
- Enable DKIM signing.
- In Google Workspace, generate 2048-bit DKIM keys.
- Apply per domain (rotate annually).
- Publish a DMARC monitoring policy.
Start with:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com
Success Metrics:
- SPF validated
- DKIM signing active
- DMARC policy published
Challenges & Fixes:
- Issue: SPF > 10 lookups.
- Fix: Flatten SPF (use subincludes or consolidation tools).
Week 2: Core Implementation
Goals: Verify Gmail alignment and test real deliverability.
Action Items:
- Check alignment.
- Ensure “From:” domain matches SPF and DKIM alignment.
- Use Gmail Postmaster Tools for validation.
- Run test sends.
- Use MailTester or GlockApps to test inbox placement.
- Adjust headers or DNS if flagged.
- Clean your lists.
- Remove inactive Gmail users (>180 days).
- Segment engaged vs. cold recipients.
- Monitor Gmail reputation.
- Track domain/IP reputation in Postmaster Tools.
- Track domain/IP reputation in Postmaster Tools.
Success Metrics:
- SPF/DKIM pass 100% of tests.
- Spam complaint rate <0.1%.
- Domain reputation = “High” or “Medium.”
Challenges & Fixes:
- Issue: DKIM fails with third-party senders.
- Fix: Add their DKIM CNAME records to your DNS.
Week 3: Optimization & Testing
Goals: Improve Gmail deliverability by refining sending practices.
Action Items:
- Implement engagement-based sending.
- Focus on active Gmail users.
- Send re-engagement campaigns to dormant users.
- Strengthen DMARC policy.
- Move from p=none → p=quarantine.
- Monitor reports for spoofed activity.
- Improve content compliance.
- Avoid spam triggers in subject lines.
- Keep text-to-image ratio balanced.
- Test sending reputation.
- Run A/B subject line tests.
- Track CTR vs. spam complaint correlation.
Success Metrics:
- Open rates increase by 10–20%.
- DMARC reports show <5% failures.
- Engagement signals trending upward.
Challenges & Fixes:
- Issue: Gmail “Promotions tab” filtering.
- Fix: Personalize content, reduce links, and maintain clean HTML.
Week 4: Advanced Strategies & Scaling
Goals: Harden security and future-proof against Gmail’s next updates.
Action Items:
- Enforce strict DMARC.
- Move to p=reject.
- Block unauthorized sources permanently.
- Deploy BIMI.
- Add a verified logo to display in Gmail inboxes.
- Requirements: DMARC enforcement + VMC (Verified Mark Certificate).
- Adopt advanced authentication.
- Implement ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) for forwarding.
- Rotate DKIM keys automatically.
- Monitor continuously.
- Automate DMARC report analysis with Dmarcian or Valimail.
- Review Google Postmaster weekly.
Success Metrics:
- Gmail inbox placement consistently 90%+.
- Spam complaints <0.05%.
- Logo (BIMI) visible in inbox.
Challenges & Fixes:
- Issue: Spoofing persists even after DMARC enforcement.
- Fix: Combine DMARC with third-party anti-phishing services (Proofpoint, Mimecast).
What to Expect After 30 Days
- Week 1: Basic compliance – no immediate inbox boost.
- Week 2: Authentication alignment – fewer rejections.
- Week 3: Engagement improves, inbox rates rise.
- Week 4: Long-term deliverability and brand trust fully established.
Pro Tip: Gmail deliverability isn’t a one-time project. It’s a cycle: Authenticate → Test → Monitor → Adapt. Following this 30-day blueprint ensures you not only meet Gmail’s 2025 rules but also stay ahead of upcoming changes.
Expert-Level Gmail Authentication in 2025

Once your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC basics are in place, it’s time to step into advanced territory. Gmail’s spam filters in 2025 are more AI-driven and reputation-sensitive than ever, which means only senders who adopt cutting-edge authentication and engagement strategies will consistently land in the inbox.
Below are the advanced tactics that professionals, enterprises, and high-volume marketers use to stay ahead.
1. Implement BIMI for Brand Recognition
What it is:
BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification) allows your logo to appear in Gmail inboxes alongside authenticated messages.
Why it matters:
- Increases trust and recognition.
- Improves open rates (studies show BIMI logos increase open rates by 10–20%).
- Requires strict DMARC enforcement (p=quarantine or p=reject).
How to set it up:
- Create an SVG logo file.
- Obtain a Verified Mark Certificate (VMC).
- Publish a BIMI DNS record.
Pro Tip: Pair BIMI with Google Workspace to strengthen your brand identity in Gmail.
2. Adopt ARC (Authenticated Received Chain)
What it is:
ARC preserves authentication results when emails are forwarded or passed through mailing lists.
Why it matters:
- Without ARC, forwarded messages often fail DKIM/DMARC checks.
- ARC ensures your authentication “travels” with the email.
Best for:
Businesses using forwarding, CRMs, or third-party senders.
3. Automate DKIM Key Rotation
Why it matters:
- Keys older than 12 months weaken security.
- Google recommends rotating DKIM keys every 6–12 months.
How to implement:
- Use automation tools like Valimail or Dmarcian.
- Schedule DNS updates quarterly to rotate keys seamlessly.
Pro Tip: Rotate keys during low-traffic hours to avoid disruption.
4. Use AI-Powered Deliverability Testing
The shift in 2025: Gmail now uses machine learning to predict spam based on sending behavior patterns. Traditional tests aren’t enough.
Advanced tools:
- SendForensics AI Scoring – predicts how Gmail will score your message.
- Inbox Monster – simulates real Gmail inbox environments.
- GlockApps AI testing – runs Gmail-specific spam simulations.
Why it works:
AI testing uncovers issues before Gmail penalizes your domain.
5. Build a Multi-Domain Sending Strategy
Why advanced senders use this:
- Isolates transactional vs. marketing email traffic.
- Protects main domain reputation.
- Helps with Gmail’s domain-specific scoring.
Example:
- marketing.yourdomain.com for newsletters.
- alerts.yourdomain.com for transactional emails.
6. Monitor Gmail-Specific Engagement Signals
In 2025, Gmail weighs recipient engagement more than ever:
- Replies > Opens > Clicks > Deletes > Spam reports.
Advanced strategies:
- Trigger automated reply campaigns (“Thanks for joining…”).
- Encourage Gmail users to drag your email into Primary tab.
- Track engagement by domain (separate Gmail metrics from Yahoo/Outlook).
7. Stay Ahead of Gmail’s Policy Updates
Google updates its sender guidelines quarterly. Common shifts include:
- Stricter thresholds for complaint rates.
- Mandatory DMARC for bulk senders.
- New AI-based reputation scoring.
Pro Tip: Bookmark Google’s Postmaster Blog and join security mailing lists like M3AAWG to stay ahead.
8. Insider Expert Secrets
From real-world experience managing Gmail deliverability for enterprises:
- Warm-up never ends. Even established domains must ramp carefully after inactivity.
- Don’t chase volume too fast. Gmail penalizes sudden surges.
- User-driven trust signals (replies, whitelists, address book additions) carry huge weight in 2025.
- Security alignment (SPF/DKIM/DMARC + TLS + BIMI) = Gmail’s gold standard.
The Gmail Deliverability Success Framework
By now, you’ve learned the foundations, the strategies, and the advanced techniques of Gmail authentication in 2025. But even the best senders stumble when they ignore the common pitfalls or forget the golden rules of deliverability. This final section pulls everything together into a success framework that ensures your emails stay trusted, secure, and consistently land in the inbox.

- Publishing multiple SPF records
- Gmail only recognizes one. Duplicate records cancel each other out.
- Gmail only recognizes one. Duplicate records cancel each other out.
- Leaving DMARC at “none” forever
- Monitoring-only mode leaves you open to spoofing and phishing.
- Monitoring-only mode leaves you open to spoofing and phishing.
- Using weak DKIM keys (1024-bit or less)
- Gmail recommends 2048-bit for proper security.
- Gmail recommends 2048-bit for proper security.
- Not aligning domains
- If “From:” domain doesn’t match your SPF/DKIM domains, Gmail downgrades your reputation.
- If “From:” domain doesn’t match your SPF/DKIM domains, Gmail downgrades your reputation.
- Ignoring engagement signals
- Even if authentication passes, high spam complaints or low opens will bury you in Promotions or Spam.
- Even if authentication passes, high spam complaints or low opens will bury you in Promotions or Spam.
Golden Rules That Always Work
- One SPF record only. Consolidate all senders into it.
Rotate DKIM keys regularly. Treat them like passwords. - Enforce DMARC. Start with quarantine, end with reject.
- Segment traffic by domain. Keep marketing and transactional emails separate.
- Monitor Postmaster Tools weekly. Google gives you the data – use it.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
- Emails landing in Promotions tab:
→ Reduce links, personalize content, encourage replies. - High spam complaints:
→ Re-engage inactive users or remove them entirely. - Authentication failures in forwarded mail:
→ Implement ARC to preserve your trust chain. - Sudden drop in Gmail inbox placement:
→ Check for expired DKIM keys, DNS misconfigurations, or policy updates.
Maintaining Long-Term Success
Deliverability isn’t a one-off project – it’s ongoing maintenance. Build a simple routine:
- Weekly: Check Postmaster Tools for spikes in complaints.
- Monthly: Review DMARC reports for unauthorized senders.
- Quarterly: Rotate DKIM keys and audit your SPF record.
- Annually: Refresh your entire authentication stack and stay updated with Gmail’s rule changes.
Final Takeaway
The most effective Gmail deliverability framework is simple but powerful:
Authenticate → Monitor → Optimize → Enforce.
If you master DMARC, SPF, and DKIM basics, avoid the common mistakes, and apply best practices consistently, Gmail will reward you with what every sender wants: high inbox placement, trusted branding, and long-term email success.